GEODesign was retained to evaluate the structural geologic conditions of the existing rock face, identify potential stabilization concepts and design the rock slope stabilization measures. We subcontracted Scarptec, Inc. to assist with the rock face evaluation and stabilization design. Primary project challenges included:
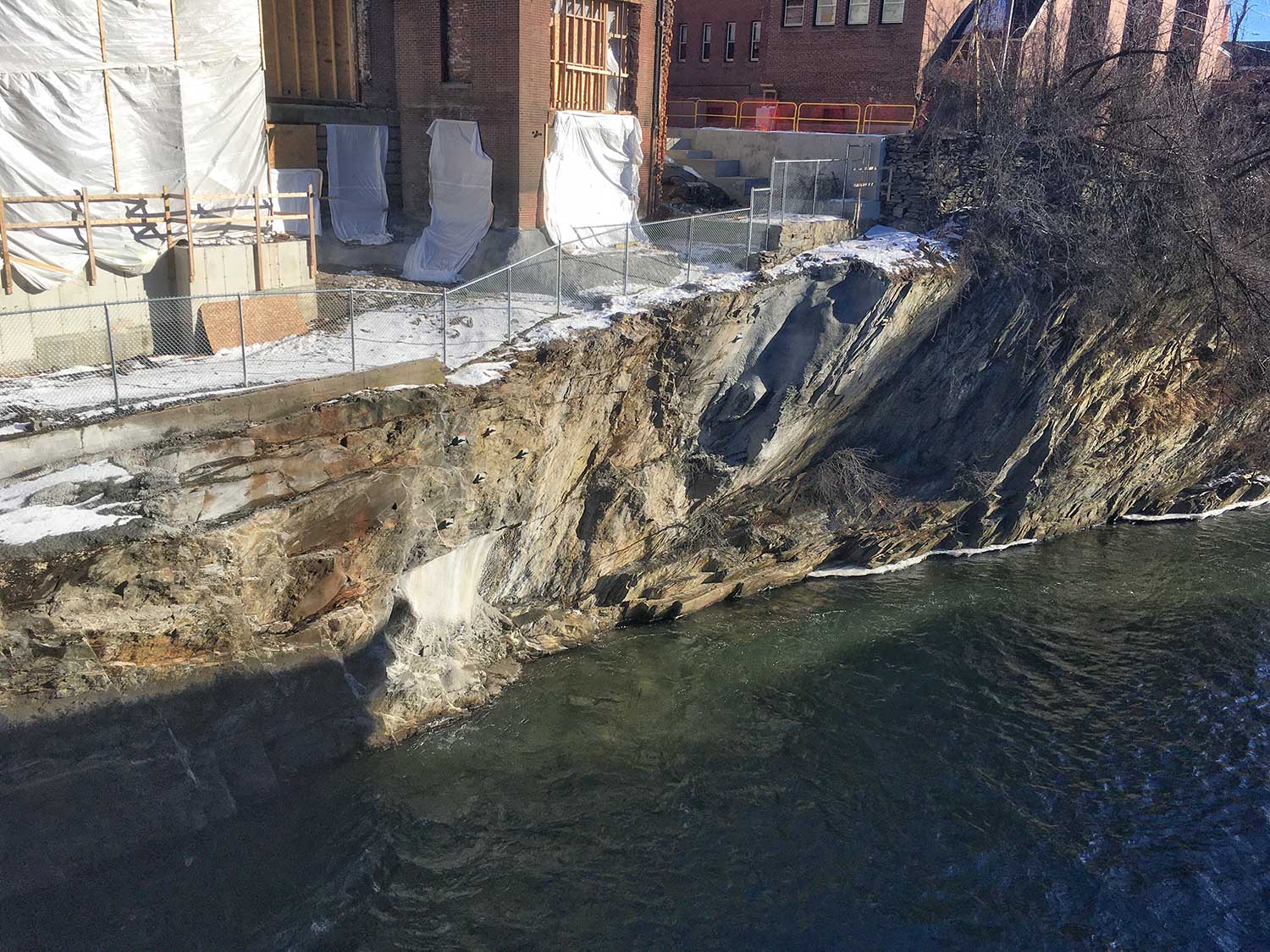
- Overhanging and back-battered rock slope with structural geologic conditions which were subject to potential long-term instability;
- Difficult access for investigation and construction work due to the local slope height, river conditions and adjacent bridge;
- Consideration of new retaining wall loads;
- Consideration of hydrostatic pressure and scour protection during peak river flows;
- Incorporation of adaptable stabilization measures to allow for construction-phase field adjustments.
The Solutions Unearthed
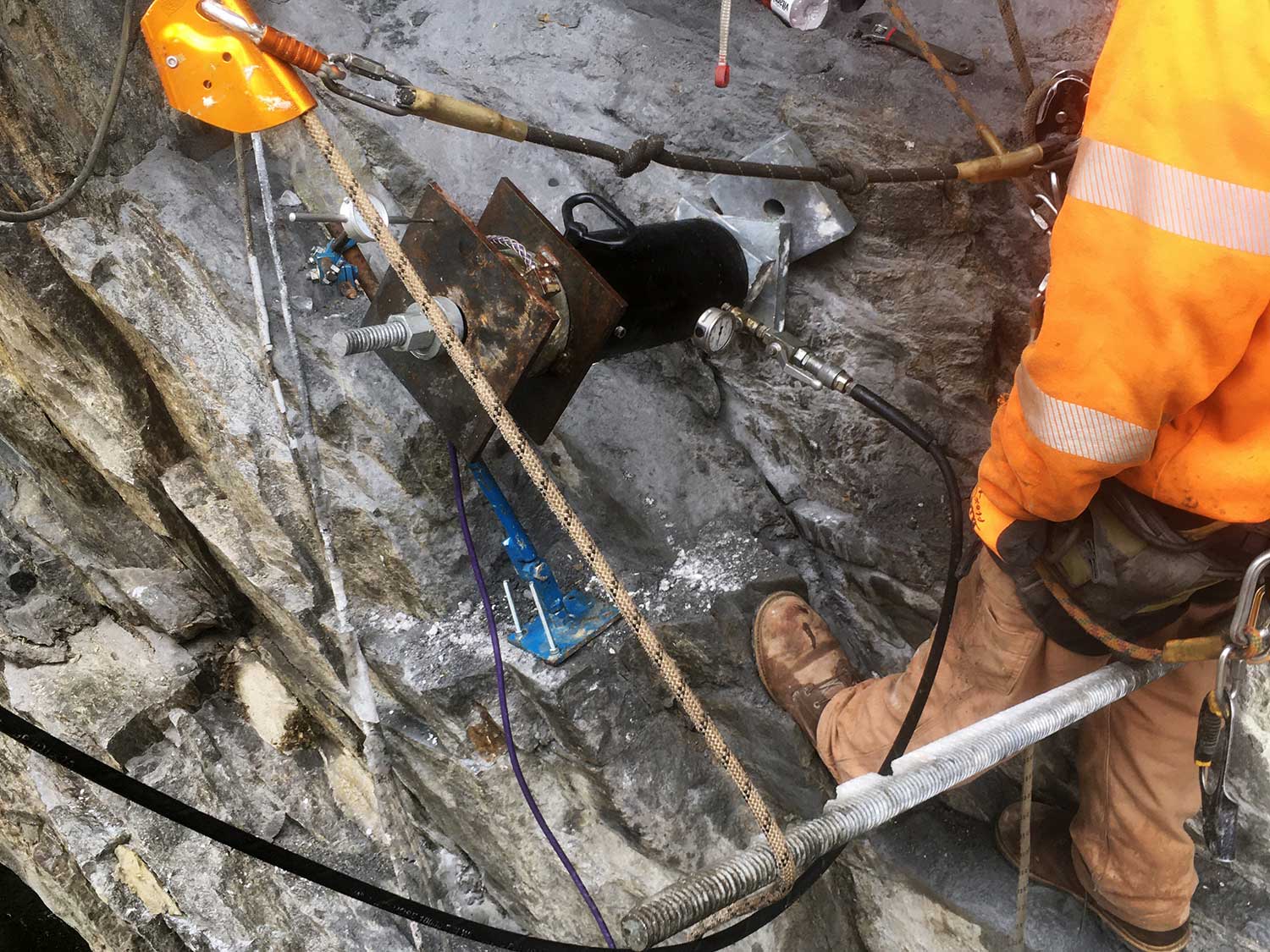
- Rock mapping and stereonet plotting was a critical step in characterizing the rock mass and discontinuities to determine mostly likely failure modes and develop appropriate stabilization measures.
- Following data collection, slope stability was evaluated using kinematic analyses to assess possible rock slope failure modes including flexural toppling, block toppling, planar sliding and wedge sliding.
- Based on field observations and analysis results, a rock slope stabilization scheme was developed which included the following measures: (1) Scaling loose surficial rock and stripping woody vegetation; (2) Localized rock doweling to support rock blocks; (3) Use of reinforced shotcrete to support overhanging rock blocks, reduce scour action, and reduce long-term weathering and joint deterioration; and (4) Vertical doweling of the new retaining wall footing to reduce thrust forces on top of the rock face.
- Stabilization element locations and quantities were finalized during construction after scaling of the rock face was complete.
Client: Housing Vermont